Types of DC Motor and its equations

DC motors are classified into several types, similar to DC generators. The DC motors are classified into three types based on the method in which the field windings are excited. You can also compare the types of a motor with the different types of DC Generator.

Before getting into the topic, learn about the construction of DC machines and the working of DC motor.
Permanent magnet DC motor
As the name indicates, the motor has a permanent magnet on the inner periphery of the stator. The necessary magnetic field required to produce the rotating torque is developed by the set of permanent magnets.
The magnets are radially magnetized inside the yoke. The stator is used to carry the magnetic field produced by the magnets. The rotor consists of armature core, armature winding, commutator and brush arrangements to carry the current into the motor.

Because of the absence of field winding, the PMDC motor has more advantages. It does not require an excitation current for field winding, which reduces the loss. PMDC motors are smaller in size and it is cheaper in cost.
Magnetic material like somarium cobalt, neodymium magnets having high residual flux and high coercivity is used as a permanent magnet. This will greatly reduce the demagnetization of permanent magnets due to excessive armature current.
PMDC motors are used extensively in automobiles for wipers, washers, blowers, air conditioners. It is also used in disc drives in personal computers.
Separately excited DC motor
In a separately excited dc motor, a separate DC supply is given to both the field winding and armature winding. Both are electrically isolated and have separate voltage ratings.

From the circuit, Armature current, Ia = Line current, I
Back emf developed,
![]()
Power drawn from the supply,
![]()
Mechanical Power developed, Pm =Input power – Losses in the armature
![]()
Where EbIa is the electrical equivalent of mechanical power developed in the motor shaft.
Self-excited DC motor
The field winding is energized by the residual magnetism and then by the emf induced in the motor. Because of the residual flux, the motor starts to rotate.
The self-excited motors are classified into three types, based on the way of connecting the field and armature winding: Shunt motor, Series motor and compound motor.
Shunt DC motor
The word ‘shunt’ means ‘parallel’. It is because the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature winding. The field winding has more number of turns with thin wire to provide high resistance. Thus the field current is much less compared to the armature current.
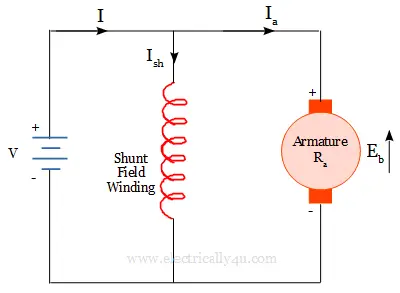
From the circuit, the current and voltage equations are,
Input current,
![]()
Current through field winding,
![]()
Back emf developed,
![]()
Power drawn from the supply, P = VI
Mechanical Power developed, Pm =Input power – Losses in the armature and field winding
![]()
![]()
Series DC motor
The field winding is connected in series with the armature winding to make DC series motor. The field winding has a lesser number of turns with thick wire. It offers low resistance for the flow of current through the armature.

The current and voltage equations of series motor are,
Since it is a series circuit, the line current, series field current and armature current are the same. Hence, I = Ise = Ia.
Back emf developed,
![]()
Power drawn from the supply, P = VI
Mechanical Power developed, Pm =Input power – Losses in the armature and field winding
![]()
![]()
Compound DC motor
Compound DC motor is a types of DC motor, which has both the shunt field winding and series field winding. Among the fluxes produced by both these windings, the shunt field flux is stronger than the series field winding.
If the flux produced by the series field winding strengthens the shunt field flux, it is called a differential compound motor. The flow of direction of current is the same in both the field windings.
On the other side, if the series field flux weakens the shunt field flux, it is called cumulatively compound motor. For this case, the flow of current is opposite in both the windings.
DC Compound motor can be further classified into two different types based on the way of connection.
Long shunt compound motor
The shunt field winding is connected in parallel with a combination of series field winding and armature conductors.

Following are the equations derived from the circuit of the long shunt compound motor.
The line current, I = Ish + Ise and Ise = Ia
Current through field winding,
![]()
Power drawn from the supply, P = VI
Back emf developed,
![]()
Short shunt compound motor
In short shunt DC compound motor, the armature winding and the shunt field winding are connected in parallel. This pair is again connected in series with the series field winding to construct the machine.

Similar to the long shunt compound motor, the equations are derived as follows.
Line current is given by,
![]()
Power drawn from the supply, P = VI
Back emf developed,
![]()